The CSRD has been in effect since 5 January 2023 and governs how EU businesses, and EU subsidiaries of non-EU companies, report on the environmental and social impact of their activities. It replaces and expands the existing requirements of the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD), which came into force in 2016.
This at-a-glance guide helps you identify your reporting requirements as a business:
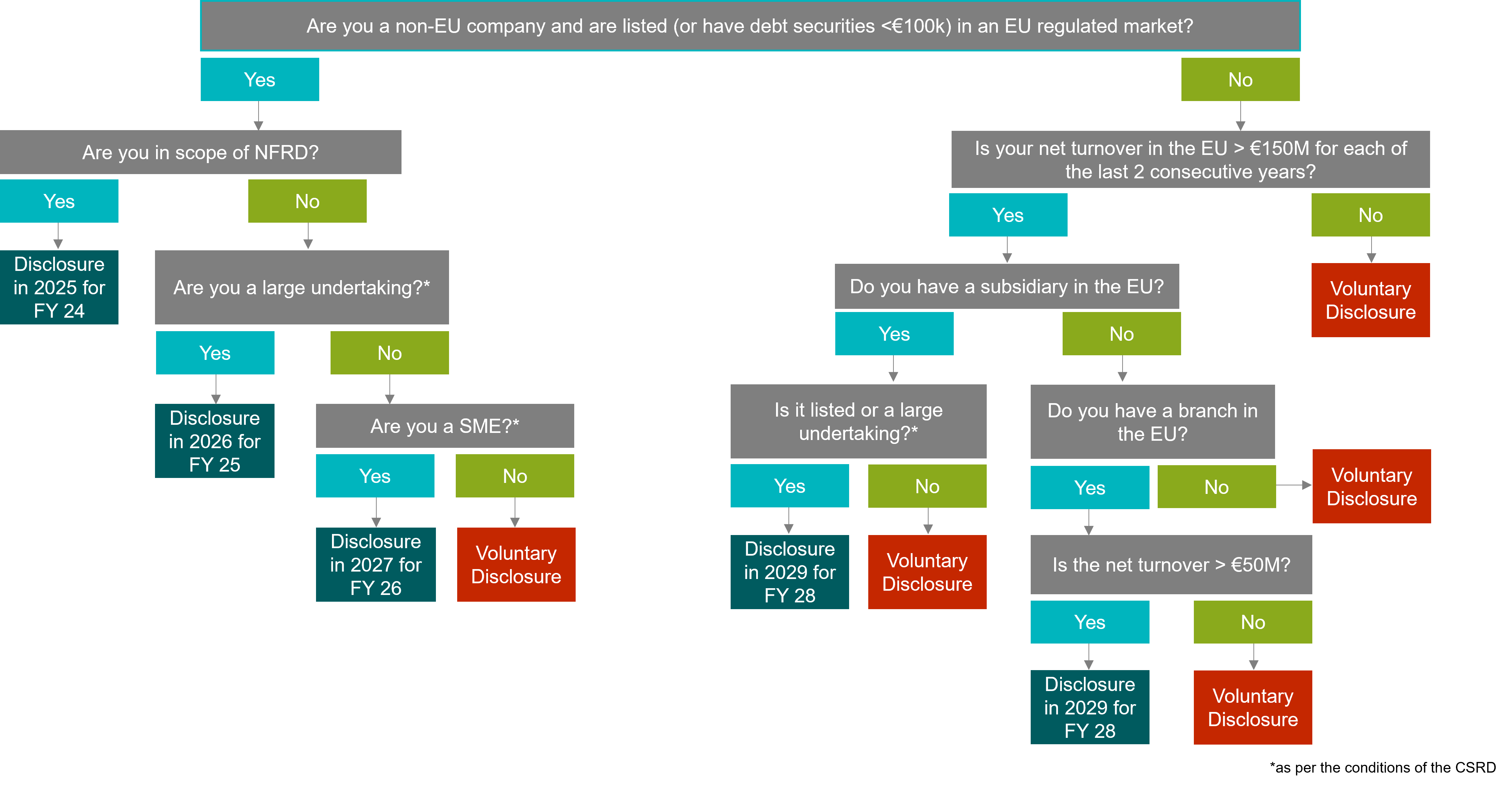
*A large undertaking is an EU company that exceeds at least two of the following three criteria on its balance sheet date:
Balance sheet total: €25 million.
Net turnover: €50 million.
Average number of employees during the financial year: 250.
* In the EU a SME is a business with fewer than 250 employees, and a turnover of less than €50 million, or a balance sheet total of less than €43 million.
* NFRD stands for Non-financial reporting directive and it requires public interest companies in EU Member states with more than 500 employees to disclose certain types of non-financial and diversity information in their yearly management reports.
BCorp Certification – B in BCorp stands for Benefit for all – B Corp Certification is a designation that a business is meeting high standards of verified performance, accountability, and transparency.
CDP – formerly Carbon Disclosure Project – CDP is a not-for-profit charity that runs the global disclosure system for investors, companies, cities, states and regions to manage their environmental impacts. It holds the largest repository of greenhouse gas emissions and energy use data in the world.
CDSB – Climate Disclosures Standards Board – The CDSB is an international consortium of business and environmental NGOs committed to advancing and aligning the global mainstream corporate reporting model to equate natural capital with financial capital.
COP – Conference of the Parties – The annual conference of the parties to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change. The COP summits bring parties (mainly governments) together to accelerate action towards the goals of the Paris Agreement, signed in 2015 by 196 parties, and the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change.
CSRD – Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive – CSRD is an EU ESG (environmental social governance) standard passed by European Union Council on 28 November 2022 designed to make corporate sustainability reporting more common, consistent, and standardised like financial accounting and reporting.
ESRS – European Sustainability Reporting Standards – ESRS are standards that define the rules of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). ESRS aim to advance the scope and quality of corporate sustainability reporting and promote sustainable development through transparency.
EU Taxonomy – EU Sustainable Finance Taxonomy – The EU taxonomy for sustainable activities is a classification system established to clarify which investments are environmentally sustainable, in the context of the European Green Deal. The aim of the taxonomy is to prevent greenwashing and to help investors make greener choices.
GHG Protocol – Greenhouse Gas Protocol – GHG Protocol provides standards, guidance, tools and training for business and government to measure and manage climate-warming emissions.
GRESB – Global Real Estate Sustainability Benchmark – Private and public institutional investors look to GRESB’s annual survey as the barometer of sustainability performance in the commercial real estate industry.
GRI – Global Reporting Initiative – GRI was announced as the official reporting standard of the United Nations Global Compact, making it the default reporting framework for the company’s more than 5,800 associated companies.
IASB – International Accounting Standards Board – The International Accounting Standards Board is the independent accounting standard-setting body of the International Financial Reporting Standards Foundation. The IASB was founded on 1 April 2001, as the successor to the International Accounting Standards Committee.
IFC – International Finance Corporation – The IFC is an international financial institution that offers investment, advisory, and asset-management services to encourage private-sector development in less developed countries.
IFRS – International Financial Reporting Standards – A not-for-profit, public interest organisation established to develop enforceable and globally accepted accounting and sustainability disclosure standards.
IPCC – Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change – The United Nations’ body for evaluating scientific climate change information. The IPCC releases regular reports on climate impacts and risk and offers options for mitigation and adaptation.
IR/IRRC – Integrated Reporting aka International Integrated Reporting Council – The IRRC is a global coalition of regulators, inventors, companies, standards setters, the accounting profession, academia and NGOs. The coalition promotes communication about value creation as the next step in the evolution of corporate reporting.
ISSB – International Sustainability Standards Board – In November 2121, COP26 announced the launch of ISSB. It seeks to establish a global baseline for sustainability reporting. It also applies the financial materiality concept.
NFRD – Non-financial reporting directive – NFRD requires public-interest companies in EU member states with more than 500 employees to disclose certain types of non-financial and diversity information in their yearly management reports.
OECD – Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development – OECD is a unique forum where the governments of 37 democracies with market-based economies collaborate to develop policy standards to promote sustainable economic growth. The OECD provides a setting where governments can compare experiences, seek answers to common challenges, identify good practices, and develop high standards for economic policy.
PCAF – Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials – PCAF is a global partnership of financial institutions that work together to develop and implement a harmonised approach to assess and disclose the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with their loans and investments.
PRI – (UN) Principles for Responsible Investment – PRI is a United Nations-supported international network of financial institutions working together to implement its six aspirational principles, often referenced as “the Principles”.
SASB – Sustainability Accounting Standards Board – SASB offers disclosure standards for more than 75 industries to ensure information disclosed is most relevant to the financial performance of the organisation’s industry. The standard focus on financially material aspects so that the disclosure can help drive business and investment decisions.
SBTi – Science Based Targets initiative – SBTi defines and promotes best practices in emissions reductions and net-zero targets in line with climate science.
SDGs – Sustainable Development Goals – The SDGs are a United Nations initiative with 17 goals to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure peace and prosperity for all by 2030. The SDGs include 169 targets to be measured by 232 indicators.
SFDR – Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation – SFDR is the European Union’s attempt to harmonise ESG disclosure standards across the continent. It provides a comprehensive sustainability disclosure requirement covering a wide range of environmental, social and governance metrics and criteria.
TCFD – Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosure – TCFD was created in 2015 by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) to develop consistent climate-related financial risk disclosures for use by companies, banks and investors in providing information to stakeholders.
UNGC – UN Global Compact – UNGC asks companies to first do business responsibly and then pursue opportunities to solve societal challenges through business innovation and collaboration.
VRF – Value Reporting Foundation – VRF is a global non-profit organisation that offers a comprehensive suite of resources designed to help businesses and investors develop a shared understanding of enterprise value – how it is created, preserved or eroded over time.
WEF – World Economic Forum – WEF is the international organisation for public-private co-operation which engages the foremost political, business, cultural and other leaders of society to shape global, regional and industry agendas including ESG investing or sustainable responsible investing.


To discover for yourself what makes us the bright alternative and how we can support, please contact Katrina Magsino, our ESG Client Services Manager.